跨链消息传递
Scroll 有任意消息传递的跨链桥,可实现代币传输,并允许去中心化应用在 Layer 1 和 Layer 2 之间进行通信。这意味着Layer 1的去中心化应用可以触发 Layer 2 的合约方法,反之亦然。接下来,我们将解释如何在 Layer 1 和 Layer 2 之间中继消息。
从 L1 向 L2 发送消息
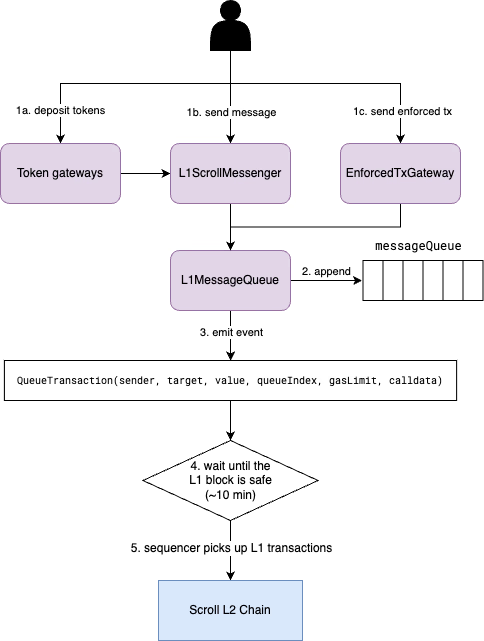
将消息从 L1 发送到 L2 有两种主要方法:
通过L1ScrollMessenger合约发送任意消息,或是通过 EnforcedTxGateway 合约发送强制交易。
这两种方法都允许用户在 L1 上发起 L2 交易,并在 L2 上调用任意合约。
对于任意消息,L2 交易的发送方是别名,是 L1ScrollMessenger 合约的地址。
对于强制交易,L2 发送方是外部所有者帐户(EOA)。
此外,我们还提供多种标准代币网关,使用户更容易存入ETH和其他标准代币,包括ERC-20、ERC-677、ERC-721和ERC-1155。
从本质上讲,这些网关将代币存款编码为消息,并通过 L1ScrollMessenger 合约将其发送给 L2 上的对应方。
你可以在存款网关中找到更多关于 L1 代币网关的信息。
如图 1 所示,任意消息和强制交易都将增加到存储在 L1MessageQueue 合约的消息队列中。合约 L1MessageQueue 提供两个方法 appendCrossDomainMessage,appendEnforcedTransaction 分别用于添加任意消息和强制交易。
/// @notice Append an arbitrary L1-to-L2 message into this contract./// @param target The target address on L2./// @param gasLimit The maximum gas can be used for this transaction on L2./// @param data The calldata of the L1-initiated transaction.function appendCrossDomainMessage( address target, uint256 gasLimit, bytes calldata data) external;
/// @notice Append an enforced transaction to this contract./// @param sender The sender address of this transaction./// @param target The target address of this transaction./// @param value The value to be transferred on L2./// @param gasLimit The maximum gas should be used for this transaction on L2./// @param data The calldata of the L1-initiated transaction.function appendEnforcedTransaction( address sender, address target, uint256 value, uint256 gasLimit, bytes calldata data) external;这两个方法都使用 Scroll 链中引入的新交易类型 L1MessageTx 构造 L1 发起的交易,并计算交易哈希(更多详细信息请参阅L1 消息交易中)。
随后,L1MessageQueue 将交易哈希增加到消息队列中,并发出事件 QueueTransaction(sender, target, value, queueIndex, gasLimit, calldata)。
在构造 L1 消息交易时,appendCrossDomainMessage 和 appendEnforcedTransaction 的区别是:
appendCrossDomainMessage只能被L1ScrollMessenger合约所调用,并且其msg.sender使用 别名地址,即L1ScrollMessenger地址作为交易发送方。appendEnforcedTransaction只能被EnforcedTxGateway合约所调用,并且其sender使用方法的参数作为交易的发送方。这允许用户通过跨链桥强制从 L2 提款或转账。
在 L1 上成功执行交易后,Scroll 排序器中的观察程序将监听 L1MessageQueue 合约,从 L1 区块收集新的 QueueTransaction 事件。
然后,排序器为每个事件构造一个新的 L1MessageTx 交易,并将其添加到其本地 L1 交易队列中去。
在构造新的 L2 区块时,排序器将包括来自其 L1 交易队列和 L2 内存池的交易。
请注意,L1 消息交易必须按照 L1MessageQueue 合约中的 L1 消息队列顺序,按顺序包含在区块内。
L1MessageTx 交易总是在 L2 区块排序在前,然后再是 L2 交易。
目前,我们将 L2 区块中的 L1MessageTx 交易数量限制为 NumL1MessagesPerBlock (当前设置为 10)。
接下来,我们将进一步介绍通过 L1ScrollMessenger 发送任意消息,和通过 EnforcedTxGateway 发送强制交易的具体过程。
发送任意消息
合约 L1ScrollMessenger 提供了两个 sendMessage 函数来发送任意消息。唯一的区别是第二个允许用户指定发送方地址以外的退款地址来接收手续费退款。
sendMessage 函数签名
sendMessage 函数签名/// @param target The target address on L2./// @param value The value to deposit to L2 from `msg.value`./// @param message The message passed to target contract./// @param gasLimit The maximum gas can be used for this transaction on L2.function sendMessage( address target, uint256 value, bytes memory message, uint256 gasLimit) external payable;
/// @param target The target address on L2./// @param value The value to deposit to L2 from `msg.value`./// @param message The message passed to target contract./// @param gasLimit The maximum gas can be used for this transaction on L2./// @param refundAddress The address to refund excessive fee on L1.function sendMessage( address target, uint256 value, bytes calldata message, uint256 gasLimit, address refundAddress) external payable;这两个函数都需要用户在L2上为对应的 L1MessageTx 交易提供gas上限,并预付根据gas上限计算而来的 L1 的消息中继费用。
该费用通过 L1 上的 feeVault 合约收取。
如果由于用户没有为其L1上的消息设置正确的 gas 上限而导致 L2 上的交易失败,则用户可以用更高的 gas 上限重放相同的消息。
您可以在重放失败消息部分,找到更多详细信息。但由于这些费用的任何未使用部分都会退还给用户,因此高估 gas 限制不会有任何惩罚。
sendMessage 函数将参数编码进跨链消息(请参考下面的代码片段),其中消息 nonce 是 L1 消息队列中下一条消息的索引值。然后,编码的数据将被用于在 L2 上执行的 L1MessageTx 交易中的调用数据(calldata)。
请注意,此类跨链消息始终调用 L2 上 L2ScrollMessenger 合约的 relayMessage 函数。
abi.encodeWithSignature( "relayMessage(address,address,uint256,uint256,bytes)", _sender, _target, _value, _messageNonce, _message)存入的 value 数量的 ETH 被锁定在 L1ScrollMessenger 合约中。
如果消息中的 ETH 无法支付消息中继费和存入金额,则交易将被回退。
L1ScrollMessenger 合约会将超出部分退还给指定的 refundAddress 或交易发送方。
最后, L1ScrollMessenger 通过 appendCrossDomainMessage 方法将跨链消息添加到 L1MessageQueue 中。
发送强制交易
EnforcedTxGateway 合约提供了两个 sendTransaction 函数来发送强制交易。
在第一个函数中,生成的 L1MessageTx 交易的发送方是交易发送方。
而第二个函数中,使用传入的 sender 的地址作为 L1MessageTx 交易的发送方。
这允许第三方代表用户发送强制交易并支付中继费。
请注意,第二个函数需要提供与 sender 地址匹配的生成 L1MessageTx 交易的有效签名。
这两个函数都要求 sendTransaction 发送方是外部所有者帐户(EOA)。
sendTransaction 函数签名
sendTransaction 函数签名/// @param target The target address on L2./// @param value The value to withdraw from the `tx.origin` address on L2./// @param gasLimit The maximum gas can be used for this transaction on L2./// @param data The calldata passed to target contract.function sendTransaction( address target, uint256 value, uint256 gasLimit, bytes calldata data) external payable;
/// @param sender The sender address who will initiate this transaction on L2./// @param target The target address on L2./// @param value The value to withdraw from the `sender` address on L2./// @param gasLimit The maximum gas can be used for this transaction on L2./// @param data The calldata passed to target contract./// @param signature The signature for the corresponding `L1MessageTx` transaction./// @param refundAddress The address to refund excessive fee on L1.function sendTransaction( address sender, address target, uint256 value, uint256 gasLimit, bytes calldata data, bytes memory signature, address refundAddress) external payable;与任意消息中继类似, sendTransaction 扣除消息中继费用后将其转入L1的 feeVault 账户。
但一个关键的区别是,传递给函数的 value 代表的是发送方账户在 L2 上要转账的 ETH 数量,而不是在 L1 上。
因此, msg.value 只需要支付消息中继费。
如果消息中的ETH数量无法支付费用,那么交易将失败。
在第一个函数中,任何多余的费用将退还给交易发送方,在第二个函数,将退还给 refundAddress 地址。
最后, EnforcedTxGateway 将调用 L1MessageQueue.appendEnforcedTransaction 将交易添加到消息队列中。
重放失败消息
如果由于gas不足而导致L2上的 L1MessageTx 交易失败,用户可以用更高的gas上限重放消息。
L1ScrollMessenger 合约提供了 replayMessage 方法,允许用户发送与上一个失败消息相同的信息 ,但有更高的 gas 上限。
该消息将成为 L2 上新的一条 L1MessageTx 交易。
请注意,我们不会退还上一条失败交易的gas费,因为它已经在L2上进行处理。
replayMessage 函数签名
replayMessage 函数签名/// @param from The address of the sender of the message./// @param to The address of the recipient of the message./// @param value The msg.value passed to the message call./// @param queueIndex The queue index for the message to replay./// @param message The content of the message./// @param newGasLimit New gas limit to be used for this message./// @param refundAddress The address of account who will receive the refunded fee.function replayMessage( address from, address to, uint256 value, uint256 queueIndex, bytes memory message, uint32 newGasLimit, address refundAddress) external payable;由于 L2ScrollMessenger 合约记录了成功中继到 L2 的所有 L1 消息,因此如果原始消息成功,重放消息交易将在 L2 上被回退。
消息中继费
部署在 L1 上的 L2GasPriceOracle 合约会在给定消息的 gas 上限的情况下,计算消息的中继费用。
该合约将 l2BaseFee 存储在其存储中,当前由 Scroll 运行的专用中继器更新。
因此,L1 到 L2 的消息中继费为 gasLimit * l2BaseFee 。
地址别名(Address Alias)
由于 CREATE 操作码,使得可以在 L1 和 L2 上的相同地址上部署字节码不同的合约。
为避免恶意用户利用此漏洞,当消息发送方是 L1 上的合约时,跨链桥会应用地址别名。
L1 消息交易的发送方地址别名为 l1_contract_address + offset offset,其中 offset 为 0x1111000000000000000000000000000000001111。
从 L2 向 L1 发送消息
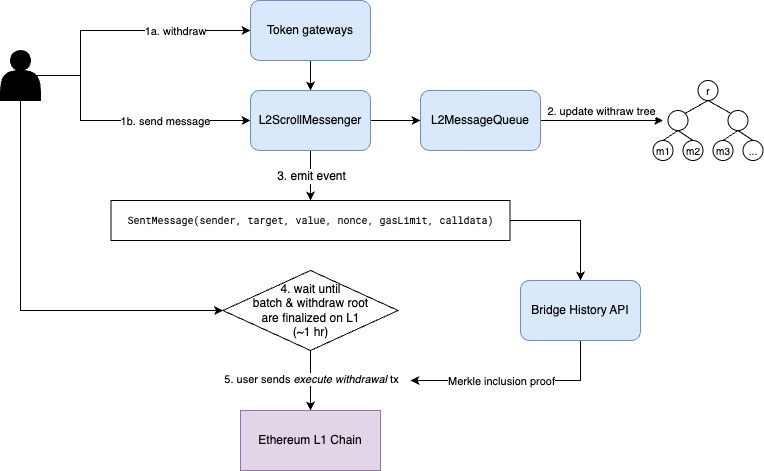
在L2上,用户可以向 L2ScrollMessenger 合约发送任意消息来提取代币并调用L1合约。与L1类似,我们构建了几个标准代币网关,以便更容易地发起代币提款。有关L2代币网关的更多详细信息,请参阅提款网关。
L2ScrollMessenger 合约还提供了一个 sendMessage 函数方法。
与 L1ScrollMessenger.sendMessage 函数的区别在于,L1ScrollMessenger.sendMessage 省略了 gasLimit 参数,因为 L1 上的提现交易由用户提交,交易费直接在 L1 上支付。
因此,L2的 sendMessage 函数要求 msg.value 等于参数 value
并将按照与 L1ScrollMessenger 相同的机制将参数编码为跨链消息。
sendMessage 函数签名
sendMessage 函数签名/// @param target The target address on L1./// @param value The value to withdraw to L1 from `msg.value`./// @param message The message passed to target contract./// @param _gasLimit Ignored in the L2ScrollMessenger because the withdrawal execution on L1 is done by the user.function sendMessage( address target, uint256 value, bytes memory message, uint256 _gasLimit) external payable;接下来, 通过调用其 appendMessage 函数将跨链消息哈希添加至 L2MessageQueue。
L2MessageQueue 合约维护了 提款树 (Withdraw Trie),一个仅支持新增的默克尔树。
每次将新消息增加至队列时,合约都会将其插入提款树并更新树的根哈希。
在 L1 的rollup合约最终确认了包含用户从L2发送至L1消息的交易批次后,
用户需要提交相应的执行提款交易,来调用 L1ScrollMessenger合约的 relayMessageWithProof 方法,在L1上执行提款。
由于默克尔树证明,L1上的提款交易的最终确认是无需信任的,可以由用户自己提交,也可以由第三方代替用户提交。
为了更容易地构建提款树的默克尔包含证明(Merkle Inclusion Proof,MIP),Scroll 维护了一个名为跨链桥历史记录 API 的服务。跨链桥历史记录 API 监听了从 L2ScrollMessenger 合约发出的 SentMessage 事件并在内部维护了一个提款树。
它不断为每条提款消息生成默克尔证明。用户和第三方服务可以从跨链桥历史记录 API 查询默克尔树证明,以包含在执行提款交易中。
请注意,执行提款交易可以由用户自己提交,也可以由第三方服务提交。
提款树
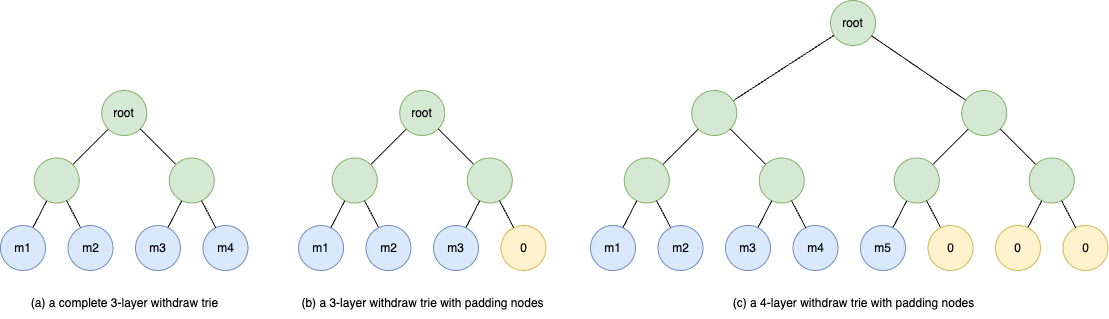
提款树是一个密集的二元默克尔树。叶节点的哈希继承自消息哈希,而非叶节点的哈希是其两个子节点的连接哈希的 Keccak 哈希摘要。 提款树的深度根据添加到树中的消息数量动态增长。
图3(a)显示了完整的三层提款树的示例。当叶子的数量不能填满一个完整的二叉树时,我们用哈希 0 填充叶节点,如图 3(b) 和 3(c) 所示。将新消息添加到不完整的提款树时,先前填充的叶节点将被具有实际消息哈希的新叶节点替换。