Deposit Gateways
This document describes how users and developers can utilize gateways to deposit tokens from L1 to L2. We provide several gateways for standard tokens and a gateway router on L1, listed in the table below.
| Gateway Contract | Description |
|---|---|
L1GatewayRouter | The gateway router supports the deposit of ETH and ERC20 tokens. |
L1ETHGateway | The gateway to deposit ETH. |
L1StandardERC20Gateway | The gateway for standard ERC20 token deposits. |
L1CustomERC20Gateway | The gateway for custom ERC20 token deposits. |
L1WETHGateway | The gateway for Wrapped ETH deposits. |
L1ERC721Gateway | The gateway for ERC-721 token deposits. |
L1ERC1155Gateway | The gateway for ERC-1155 token deposits. |
Overview
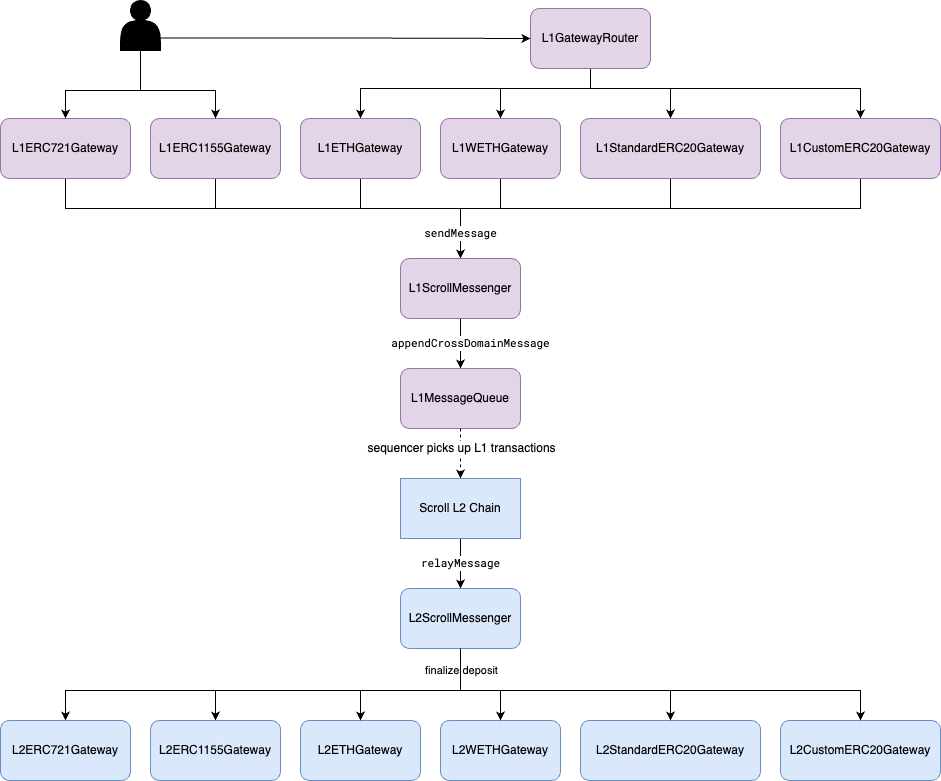
The figure depicts the deposit workflow from L1 to L2. Users call the gateways to initialize the token deposit. The deposit is then encoded into a message sent to the L1ScrollMessenger contract and a corresponding L1-initiated transaction is appended to the L1MessageQueue. To finalize the deposits on L2, the L2 sequencer collects the new L1 transaction events and includes the corresponding transactions in the L2 blocks it creates. The subsequent sections describe the details of how different tokens are deposited. You can find more details about the L1-to-L2 message relay workflow in the Cross-Domain Messaging.
Depositing ETH
Scroll treats ETH as its native token. We pre-allocate a sufficient amount of ETH to the L2ScrollMessenger contract in the genesis block so that it can transfer native ETH token to L2 accounts without minting. Depositing ETH works as follows.
-
L1GatewayRouterprovides three functions to deposit ETH from L1 to L2. ThedepositETHAndCallfunction can transfer ETH and execute a contract call at the same time.function depositETH(uint256 _amount, uint256 _gasLimit) external payable;function depositETH(address _to, uint256 _amount, uint256 _gasLimit) public payable;function depositETHAndCall(address _to,uint256 _amount,bytes calldata _data,uint256 _gasLimit) external payable; -
All three
depositETHfunctions call intoL1ETHGateway.L1ETHGatewayencodes the deposit into a message sent to theL1ScrollMessengercontract. -
The ETH of the deposit amount is locked in the
L1ScrollMessengercontract.L1ScrollMessengerappends the message to the message queue in theL1MessageQueuecontract. -
After the deposit transaction is finalized on the L1, the sequencer will include a corresponding L2 transaction in the L2 block to finalize the deposit and transfer ETH to the recipient address on L2.
-
The L2 transaction calls the
L2ScrollMessenger.relayMessagefunction, which executes the relayed message. In the case of ETH deposit, therelayMessagefunction callsL2ETHGateway.finalizeDepositETHto transfer ETH to the recipient account on L2. -
If the user calls
depositETHAndCallon L1,finalizeDepositETHin theL2ETHGatewaycontract will forward the additional data to the target L2 contract.
Depositing ERC20 Tokens
Several ERC20 gateway contracts are provided to bridge different kinds of ERC20 tokens, such as standard ERC20 tokens, custom ERC20 tokens, and Wrapped ETH token. L1GatewayRouter records the canonical mapping of ERC20 tokens to the corresponding ERC20 gateway on the L1. The L1GatewayRouter uses StandardERC20Gateway as the default ERC20 gateway for new ERC20 tokens unless a custom gateway is already set up.
The deposit of ERC20 tokens works as follows.
-
To deposit ERC20 tokens from L1 to L2, users can use
L1GatewayRouter.depositERC20andL1GatewayRouter.depositERC20AndCallshown below.function depositERC20(address _token, uint256 _amount, uint256 _gasLimit) external payable;function depositERC20(address _token, address _to, uint256 _amount, uint256 _gasLimit) external payable;function depositERC20AndCall(address _token,address _to,uint256 _amount,bytes memory _data,uint256 _gasLimit) public payable; -
Based on the mapping from ERC20 tokens to gateway, the
L1GatewayRoutercalls to the corresponding gateway:L1StandardERC20Gateway,L1CustomERC20Gateway, orL1WETHGateway. The remaining steps will be described separately.
Standard ERC20 Tokens
Standard ERC20 tokens are tokens that do not require any custom logic. For such tokens, their L2 ERC20 token contracts are created by L2StandardERC20Gateway. The remaining steps for standard ERC20 token deposit are:
- The
L1StandardERC20Gatewaycontract locks the ERC20 tokens by transferring them from the sender to itself. - If this ERC20 token hasn’t been withdrawn through
L1StandardERC20Gatewaybefore,L1StandardERC20Gatewaywill compute a deterministic L2 ERC20 token address and appends the token metadata (symbol, name, and decimals) to the message for the potential contract deployment on L2. If the L2 token address is already stored in thetokenMapping,L1StandardERC20Gatewaywill directly load the L2 token address from the mapping. L1StandardERC20Gatewayencodes the token deposit message and callsL1ScrollMessengerto send the message.- The corresponding L2 transaction calls the
L2ScrollMessenger.relayMessagefunction to finalize the deposit on L2. In the case of standard ERC20 token deposits, the transaction then callsL2StandardERC20Gateway.finalizeDepositERC20. - If this ERC20 token contract hasn’t been deployed on L2,
L2StandardERC20Gatewaywill extract the token metadata from the message and callsScrollStandardERC20Factoryto deploy the standard ERC20 token on L2. L2StandardERC20Gatewaycalls the mint function on the corresponding L2 ERC20 token contract.- If the user calls
depositERC20AndCallon L1, theL2StandardERC20Gatewaywill call the target L2 contract with additional data.
Custom ERC20 Tokens
In comparison to standard ERC20 tokens, the L2 contract of custom ERC20 tokens is deployed by the token owner. The remaining steps for custom ERC20 token deposit are:
- The
L1CustomERC20Gatewaycontract locks the ERC20 tokens on L1 by transferring them from the sender to itself. L1CustomERC20Gatewayrequires an L2 ERC20 token address present in thetokenMapping. It retrieves the corresponding ERC20 token address, encodes the token deposit message, and forwards it toL1ScrollMessenger.- The corresponding L2 transaction calls the
L2ScrollMessenger.relayMessagefunction to finalize the deposit on L2. In the case of custom ERC20 token deposits, the transaction callsL2CustomERC20Gateway.finalizeDepositERC20. L2CustomERC20Gatewaycalls the mint function on the corresponding L2 ERC20 token contract. It is required that the L2 ERC20 token contract grants mint permissions to theL2CustomERC20Gatewaycontract.- If the user calls
depositERC20AndCallon L1, theL2CustomERC20Gatewaywill call the target L2 contract with additional data.
WETH Token
We provide a custom gateway L1WETHGateway for Wrapped ETH token on L1 and record the gateway address in the L1GatewayRouter. The deposit of WETH token works as follows.
L1WETHGatewaylocks the WETH tokens by transferring them from the sender to itself and unwrapping the WETH token to native ETH token. The ETH token andmsg.value(for paying the relay fee) are then sent to theL1ScrollMessengercontract together.L1WETHGatewayencodes the token deposit message and forwards it toL1ScrollMessenger.- The corresponding L2 transaction calls the
L2ScrollMessenger.relayMessagefunction to finalize the deposit on L2. In the case of WETH token deposit, the transaction callsL2WETHGateway.finalizeDepositERC20. L2WETHGatewaywraps the deposited ETH to L2 WETH token again and transfers it to the recipient address on L2.- If the user calls
depositERC20AndCallon L1, theL2WETHGatewaywill call the target L2 contract with additional data.
Depositing ERC-721/ERC-1155 Tokens
The deposit of ERC-721 or ERC-1155 tokens works very similar to ERC20 tokens. One can use the gateways L1ERC721Gateway or L1ERC1155Gateway to deposit ERC-721 /ERC-1155 tokens from L1.
function depositERC721( address _token, uint256 _tokenId, uint256 _gasLimit) external payable;
function depositERC721( address _token, address _to, uint256 _tokenId, uint256 _gasLimit) external payable;
function depositERC1155( address _token, uint256 _tokenId, uint256 _amount, uint256 _gasLimit) external payable;
function depositERC1155( address _token, address _to, uint256 _tokenId, uint256 _amount, uint256 _gasLimit) external payable;To facilitate a large amount of ERC-721 or ERC-1155 token deposits, we also provide batch deposit functions in the L1ERC721Gateway and L1ERC1155Gateway contract via the following functions:
function batchDepositERC721( address _token, uint256[] calldata _tokenIds, uint256 _gasLimit) external payable;
function batchDepositERC721( address _token, address _to, uint256[] calldata _tokenIds, uint256 _gasLimit) external payable;
function batchDepositERC1155( address _token, uint256[] calldata _tokenIds, uint256[] calldata _amounts, uint256 _gasLimit) external payable;
function batchDepositERC1155( address _token, address _to, uint256[] calldata _tokenIds, uint256[] calldata _amounts, uint256 _gasLimit) external payable;The L2 counterpart contracts for ERC-721 or ERC-1155 tokens are L2ERC721Gateway and L2ERC1155Gateway. These are used to finalize deposits on L2.